Cooks have recipes, builders have blueprints, and handweavers have weaving drafts. There are a few different formats, but all drafts carry the same essential information. There is the tie-up box, the threading pattern, and the treadling sequence. Finally, there’s the drawdown, a graphic representation of how all the threads intersect.
The two formats I see most often are the typical American draft (e.g., Handwoven), and the Swedish draft (e.g., VÄV Magasinet). Many American drafts assume jack looms; whereas, Swedish drafts usually assume counterbalance or countermarch looms. However, any loom can weave from any draft.
As Madelyn van der Hoogt says in The Complete Book of Drafting, “Any tie-up can be used for any type of loom. Discover from the tie-up which shafts must be up and which down for each shed, and do to the loom whatever is required to get them there.”
All the draft formats have this in common: The tie-up box is the starting point. The threading pattern and treadling sequence begin at that point, and go out from there.
The Swedish draft makes perfect sense (remember, of course, I weave on Swedish countermarch looms). I picture the draft as if it is lying flat in front of me.
Becky Ashenden says in the forward to Weave Structures the Swedish Way, “With this orientation of tie-up, treadling, and threading, the draft has a direct relationship to the weaving of the fabric. The tie-up’s location in the lower right-hand corner of the draft allows all other information to match as closely as possible the physical aspects of the loom.”
Here is a comparison of the Swedish and American draft formats:
Swedish Draft

- Weft drawdown (filled-in squares show lowered warp threads, weft passing over)
- Tie-up is in lower right corner, and uses black squares to designate shafts that sink / white squares for shafts that rise
- Threading is below the drawdown
- Shafts are numbered from back of the loom to front, with the first shaft the furthest from the weaver seated at the loom
- Treadling sequence is on the right, and reads from bottom to top
- Treadles are numbered from right to left
- For a “sinking shed” loom (countermarch or counterbalance loom), use the black squares to tie up sinking shafts
- For a “rising shed loom” (jack loom), use the white squares to tie up rising shafts
American Draft
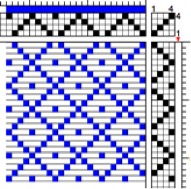
- Warp drawdown (filled-in squares show raised warp threads, weft passing under)
- Tie-up is in upper right corner, and uses numerals to designate shafts that rise / white squares for shafts that sink
- Threading is above the drawdown
- Shafts are numbered from front of loom to the back, with the first shaft the closest to the weaver seated at the loom
- Treadling sequence is on the right, and reads from top to bottom
- Treadles are numbered from left to right
- For a “sinking shed” loom (countermarch or counterbalance loom), use the white squares to tie up sinking shafts
- For a “rising shed loom” (jack loom), use the squares with numerals to tie up rising shafts
Similarities between Swedish and American Drafts
- Threading reads right to left
- Squares in the tie-up box represent treadle cords that attach treadles to corresponding shafts

Resources
Getzmann, Ulla, and Becky Ashenden. Weave Structures the Swedish Way. Shelburne, MA: Väv Stuga Press, 2006.
Hoogt, Madelyn Van der. The Complete Book of Drafting for Handweavers. Coupeville, WA: Shuttle-Craft Books, 1993.
May you flourish at your loom.
All the best,
Karen